Ethereum Layer-2
Key Takeaways
- Due to the scalability constraints on Ethereum’s mainchain (Layer-1), Layer-2s were created to scale transaction costs and throughput.
- Users demanding faster and more affordable transactions have shown a willingness to sacrifice the decentralization of Ethereum for the throughput of L2 solutions. L2-related tokens potentially represent a compelling investment to capitalize on these trends.
- While several technical approaches have attempted to build L2s, optimistic roll-ups have emerged as the preferred solution measured by users and capital flows.
- Arbitrum and Optimism have shown promising traction as the two opmistic-roll up category leaders. Current token models lack value accrual and can be considered centralized, but we believe catalysts exist on the horizon that could increase utility and demand for both tokens.
Scalability Problem
Transaction fees on Ethereum have jumped to hundreds of dollars during times of high activity, rendering the mainnet unusable for anyone without deep pockets. Ethereum can only process 7-15 transactions per second, while centralized networks like Visa can scale up to over 65k tps. Since network fees function similarly to a road with a fluctuating toll, the more congested and in demand Ethereum’s rails become, the higher the transaction costs.
According to the blockchain scalability trilemma, existing blockchain models can only have two of the following three properties: decentralization, scalability, and security. When a network optimizes for one, it must sacrifice another:
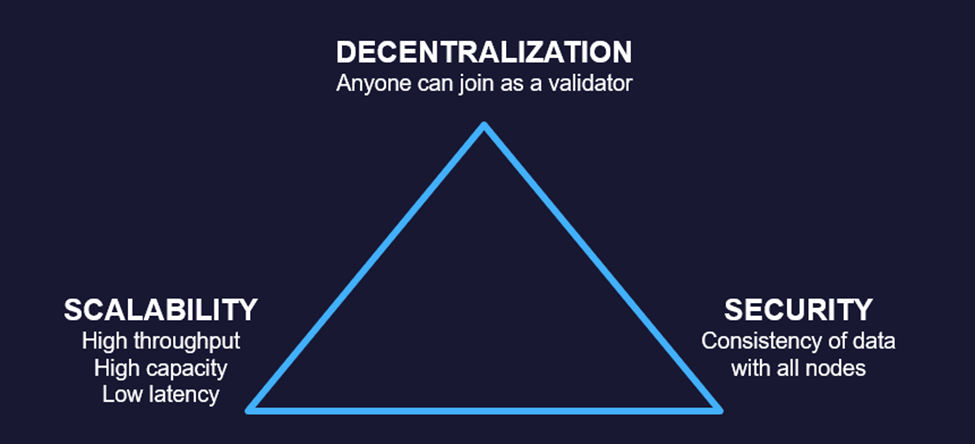
Ethereum’s high level of security and decentralization makes its block space the most expensive in crypto. On thousands of computers worldwide, the network runs software connected to the Ethereum network, known as “nodes.” Each node maintains a copy of the blockchain and verifies that it matches all the other network nodes. While this makes Ethereum’s data decentralized and secure, it sacrifices scalability since every node must sync the entire history of Ethereum’s blockchain from its first block to its most recent.
Layer-2 Solutions
Due to the scalability constraints on Ethereum’s mainchain (Layer-1), Layer-2s (L2) were created to scale transaction costs and throughput. Continuing with our toll road analogy, instead of individuals cramming separate transactions into the jam-packed single-lane highway that is Ethereum, L2s serve as mass transit solutions that batch groups of transactions and eventually settle them to the mainchain. These batches ultimately make it to the same destination as ETH native transactions but through a cheaper and more efficient route.
Layer-2 solutions enable scalability by running chains that operate separately from Ethereum but inherit some aspect of its security. Recalling the blockchain trilemma, while L2s offer scalability, they are less decentralized and secure than Ethereum. Like the mainchain, L2s have their own network of nodes verifying transactions. Decentralization varies by network but can be thought of as existing on a spectrum dependent on the diversity and extensiveness of each L2 node network. Ultimately L2s are thought to inherit the security of Ethereum since all transactions that occur on them are settled to the mainchain, where they inherit Ethereum’s immutability.
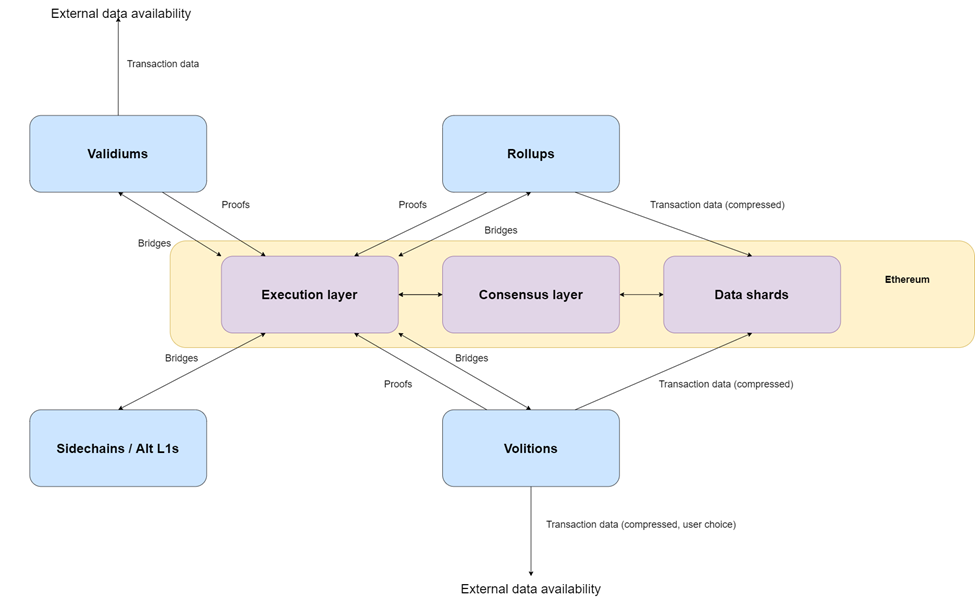
There have been several approaches to developing L2 solutions. Here are the five most popular:
- Rollups: Consolidate or “roll up” numerous off-chain transactions into a batch before forwarding them to the primary chain. Zero-knowledge rollups, or ZK-rollups, conduct off-chain computations to create “validity proofs”. Optimistic rollups assume the inherent validity of transactions and don’t produce validity proofs for each transaction bundle.
- L2s using Optimistic Rollups: Optimism, Arbitrum, Boba Network, Immutable X
- L2s using ZK Rollups: zkSYNC, Loopring, dYdX, StarkNet
- Sidechains: Functions as an independent blockchain alongside the Ethereum mainnet. Using a cross-chain bridge, they link to the main blockchain through a two-way peg.
- Sidechain Projects: Polygon, xDAI, SKALE
- State Channels: State channels are off-chain scaling techniques enabling two parties to engage in transactions without necessitating validation for each transaction from the primary chain. Essentially, a state channel functions as a multi-signature smart contract that operates solely upon receiving consent from the involved parties.
- State Channel Projects: Raiden Network, Connext Network, Celer Network
- Plasma Chains: Presents the idea of “child chains,” which stem from the primary blockchain or “root chain.” These Plasma chains resemble sidechains by linking to the Ethereum blockchain through smart contracts. To utilize a Plasma chain, you must lock ETH within a smart contract on the root chain before receiving tokens on the child chain.
- Plasma Projects: OMG Plasma, Gluon Network
- Validium: Validiums share similarities with ZK-rollups, conducting computations away from the main Ethereum layer. However, a significant distinction lies in how validiums use “off-chain data availability” instead of submitting condensed data on the main chain, which is the approach taken by ZK-rollups
- Validium Projects: DiversiFi, Immutable X
Investment Case
Each L2 model features different technical compromises and assurances. While superior technology is important, past returns in the crypto market have shown us that the projects with the best “tech” aren’t always the top performers. Often good enough tech with superior distribution, adoption, and the right narratives beats superior tech that doesn’t have these tailwinds.
There is clearly a problem and demand to scale Ethereum. Users have shown a willingness to sacrifice the decentralization of Ethereum for the throughput of L2 solutions. L2-related tokens potentially represent a compelling investment to capitalize on these trends.
As investors, we seek to understand who is winning market share, sustainably growing their network, and ultimately putting themselves in the best position to benefit from economic and user growth in a full-fledged bull market. We can use a few ecosystem metrics to understand who is winning in the competitive L2 landscape.
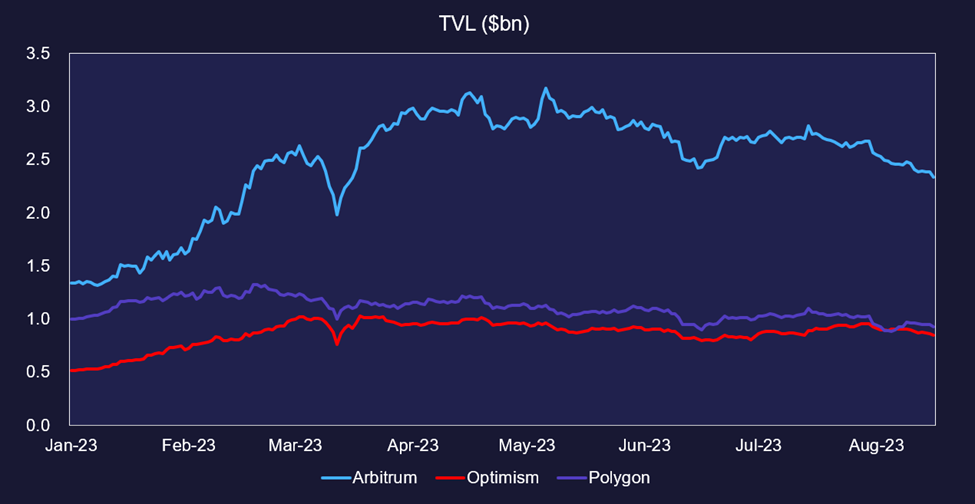
TVL
Total Value Locked (TVL) refers to the aggregate market value of assets deposited to a protocol’s smart contracts. Regarding L2s, this encompasses assets deposited to DeFi dApps built on an L2 chain. While TVL should be combined with other metrics, it helps get a high-level view of how successful a protocol has been in attracting and retaining product development and capital.
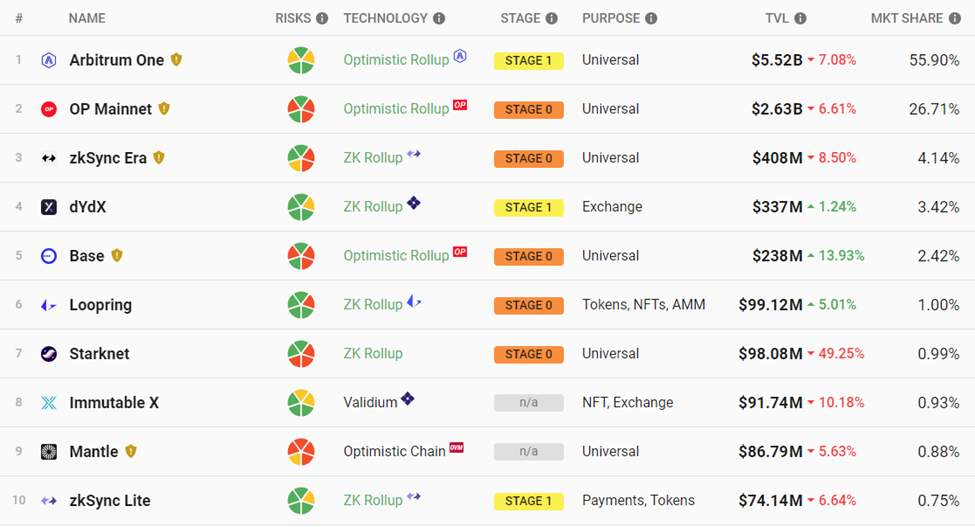
With over 80% dominance in L2 TVL, it’s clear that Optimistic Rollups are winning regarding product distribution and adoption. Polygon stands out as the one-side chain that has successfully retained a significant share of TVL. However, it is excluded from the calculation above since its sidechain operates more like an L1.
Arbitrum and Optimism successfully used airdrop campaigns to attract initial network activity. The main question with this approach was whether users would stay after they were airdropped tokens, and from a TVL standpoint, while they are not growing TVL any longer, they have successfully retained similar levels of capital to this point.
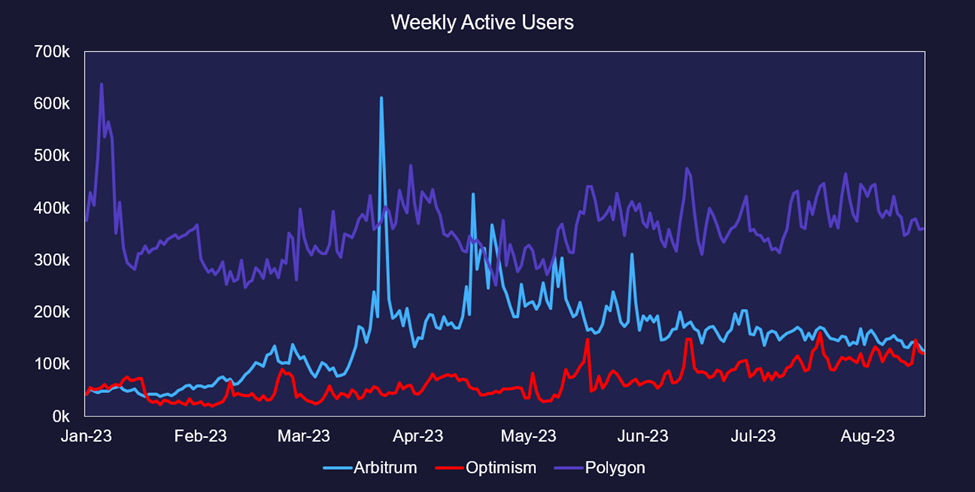
Weekly Active Users
While TVL tells how much capital has been retained, looking at active users reveals whether an L2 appeals to a broader base of crypto natives. Focusing on the big three by TVL, Optimism is the only L2 with a consistent uptrend of users, likely due to recent successful product launches from WorldCoin and Coinbase’s Base Chain. Arbitrum and Polygon are retaining a base of users but have been unable to maintain a strong uptrend. Notably, Polygon’s weekly users are down ~24% from the start of the year. Although it still retains the most extensive user base, the emergence of new products on alternative L2 ecosystems has stunted user growth.
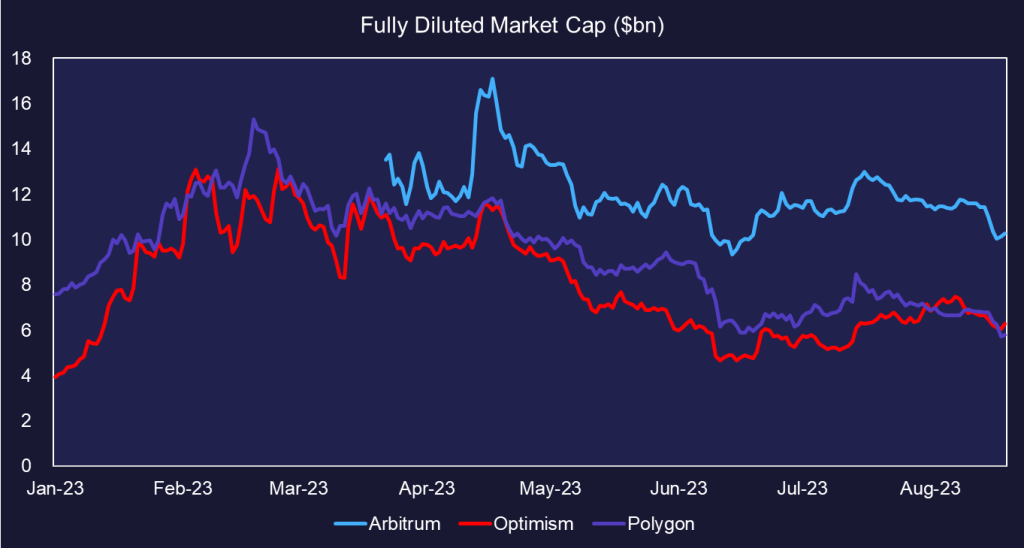
Fully Diluted Market Cap
Looking at how the market has reacted to user growth and TVL trends, Arbitrum has emerged as the most valuable protocol by fully diluted valuation. Although Aribitrum has fewer users than Polygon, because more capital is deposited per user, it is currently considered more valuable by the market. Optimism’s OP token is close to flipping Polygon by fully diluted market cap, which is notable given the token was launched several years after Polygon and has frequently traded at a discount. Note that this examines token supply on a fully-diluted basis, which accounts for all supply intended to be issued by the team.
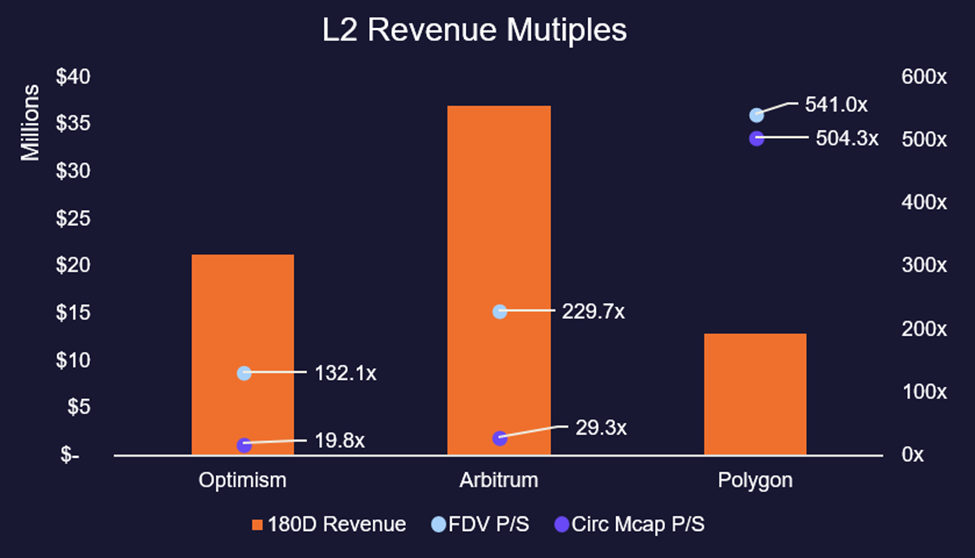
Revenue
In addition to user and economic activity, we can also look at how much fees an L2 generates to understand relative pricing with competitors. In the next section, we will go more in-depth on L2 business models, but essentially they function similarly to an L1. Users pay transaction fees to use the network, with a share of those transaction fees being used to pay Ethereum network fees and the remaining portion going to the L2 Sequencer (more below). The amount that goes to the L2 sequencer can be considered revenue, while the fees paid to the Ethereum network can be seen as a network expense. Polygon has the highest revenue multiples on both a circulating and fully diluted basis, while Optimism trades at the biggest significant discount of the three.
L2 Economics
Regarding expenses, rollup solutions like Optimism and Arbitrum include two different costs as part of their fee system. These involve the expenses associated with consolidating and publishing all transactions onto the Ethereum main chain, along with the costs of conducting transactions within the Layer 2 environment. These transactions still need to participate in a gas auction on the mainchain to secure block space, leading to unpredictable fluctuations in transaction expenses.
One of the major critiques of popular optimistic rollup L2s is their overt centralization. This centralization is key to how L2s generate revenue and scale transactions. L2 blockchains do not have validators and consensus mechanisms. Optimism and Aribitrum, both optimistic rollup chains, have block production handled by ‘sequencers.’ Sequencers are designated nodes that construct L2 blocks, maintain execution, and batch transactions to post on the Ethereum mainnet. Through its sequencers, L2s can provide close to instant transaction finality.
Optimism and Arbitrum have centralized sequencers controlled by single entities behind the project. While both plan to take steps to decentralize their sequencers, they represent a single point of failure in the present model. Sequencers collect fees retained by the protocol after paying to post transactions on Ethereum. This revenue can be considered potential value accrual for L2 projects. In their current model, ARB and OP tokens only function as governance tokens, but many expect governance could eventually vote to accrue transaction fees to token holders in some form.
Since Polygon is a proof of stake side chain instead of a true L2, its cost for settling on Ethereum is significantly lower. Through its unique set of validators, Polygon employs a method known as state sync to transmit a snapshot of its blockchain’s condition to Ethereum. While it can be seen as more decentralized from this structure, the project is evolving from simply an ETH scaling solution. The team is working on multiple networks beyond the proof of stake mainnet. These include Supernets, Avail (data availability), zkEVM, and Polygon Nightfall. While the proof of stake ETH scaling chain accrues value similar to other L1s (transaction fees), the team has not yet released details on how the upcoming upgrade will impact MATIC tokenomics.
Potential Bullish Catalysts
EIP 4844
As our recent Market Strategy note highlighted, we expect Ethereum upgrade EIP 4844 to be a potential bullish catalyst for OP and ARB 0.39% . EIP-4844 (Proto-danksharding) is expected between October 2023 and February 2024. This proposal introduces a new transaction type that permits temporary acceptance of data “blobs” on Ethereum. Unlike the current persistent data storage, these blobs are pruned after approximately two weeks to decrease the strain on the mainnet.
This EIP significantly cuts the Layer-1 costs, allowing batch data to be available for fraud proofs at a much lower cost. Estimated savings are projected to be in the range of 10x to 100x compared to current Layer-1 batch posting costs. The impact on L2s like OP and ARB cannot be understated, as data-transfer fees constitute up to 90% of fees users pay on L2 transactions. Given those fees to mainnet constitute expenses for L2s, as stated above, it is still being determined now how much of 4844’s cost savings will be passed on to users instead of accruing to the L2 tokens themselves.
Decentralizing Sequencers
Ironically Optimisms and Arbitrum’s current Achilles heel and centralizing mechanism (sequencers) are key to creating additional value accrual. Both foundations behind each protocol have alluded to decentralizing their sequencers, allowing other participants to propose and finalize L2 blocks. How this will be achieved technically remains to be seen. One potential solution would be enabling it by instituting proof of stake in the block-building process, adding additional utility to the OP and ARB 0.39% tokens by requiring them for staking. Stakers could earn transaction fees, MEV, and staking rewards, which would increase demand for protocol-related tokens.
Conclusion
We believe L2s are poised to benefit from the undeniable need to scale Ethereum. While several technical approaches have attempted to build L2s, optimistic roll-ups have emerged as the preferred solution measured by users and capital flows. The two category leaders, Arbitrum and Optimism, have shown promising traction and currently dominate with over 80% of TVL among L2s. While current token models lack value accrual and can be considered centralized, catalysts exist on the horizon that could increase utility and demand for both tokens.

