Cardano: Building Towards Sustainable DeFi
CLICK HERE for the full copy of this report in PDF format.
Executive Summary
- Cardano (ADA) is an open-source blockchain founded in 2015 that leverages a Proof-of-Stake (PoS) consensus mechanism through a protocol known as Ouroboros. It supports the development of decentralized applications (dApps) through a multi-asset ledger and smart contract functionality. ADA is the native token on Cardano and is used to transact, pay network fees, and provide security via staking.
- Peer-Reviewed Research – IO Global (IOG) is a technology consulting company and the primary developer of Cardano. In contrast to other blockchains, Cardano developers have favored a measured approach in bringing smart contract functionality to market, relying on peer-reviewed research and formal methods to build the platform. IOG believes that this strategy will result in a robust and scalable network with more sustainable incentive structures compared to other smart contract platforms. Smart contracts were enabled in September 2021 with the completion of the Alonzo upgrade.
- Unique Architecture – Cardano employs an Extended Unspent Transaction Output (EUTXO) accounting model (as opposed to an account-based model like Ethereum) for its ledger, which combines the structural simplicity of the UTXO model with the ability to execute smart contracts. The proposed advantages of the EUTXO model are greater cost predictability and the capability of processing multiple transactions in parallel. Cardano is written in Haskell, a functional programming language, which enables increased precision and traceability compared to object-oriented languages like Solidity or Rust.
- Modular Scaling – Cardano’s Layer 2 scaling solution, Hydra, adds the capacity to perform off-chain transactions and makes regular payment transactions magnitudes cheaper and faster. Hydra prevents peer-to-peer microtransactions from overloading the mainchain by allowing users to perform a series of actions off-chain and move only the final state back on-chain.
- Digital Identity and Sustainable DeFi – The north star for IOG is bringing sustainability to DeFi via digital identification metadata, which might allow community-defined best practices to emerge and reduce the attack surface for corrupt players in DeFi. The initiatives IOG is undertaking today are done with the goal of ultimately reducing scams, hacks, and exploits and eliminating corruption via trustless identity solutions.
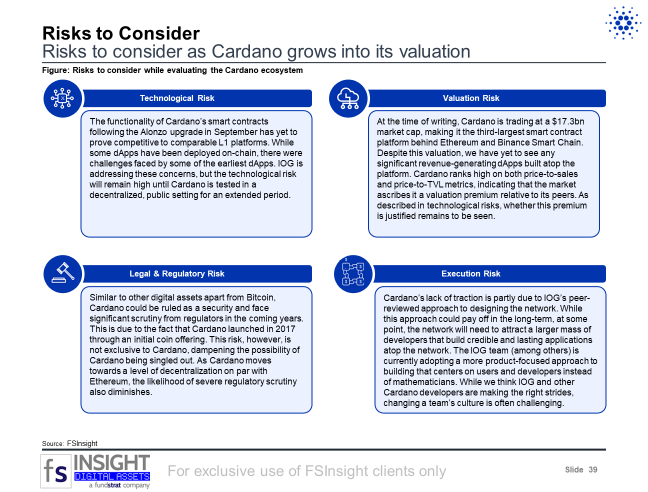
- Risks – Risks to consider when investing in Cardano: technology, valuation, regulatory, and execution.
- Bottom line – Cardano’s low time preference has resulted in a relative lack of observable traction in terms of dApps and fees paid to the network. However, IOG has defined initiatives that include mainchain bridging, native stablecoins, and the improvement of developer resources, which could lead to an influx in capital and help Cardano to grow into its valuation. The next major milestone to monitor is the Vasil hard fork later this month.
Key Slides From This Report…
Project Overview (Slide 3)
Cardano Employs Ouroboros Consensus (Slide 8)
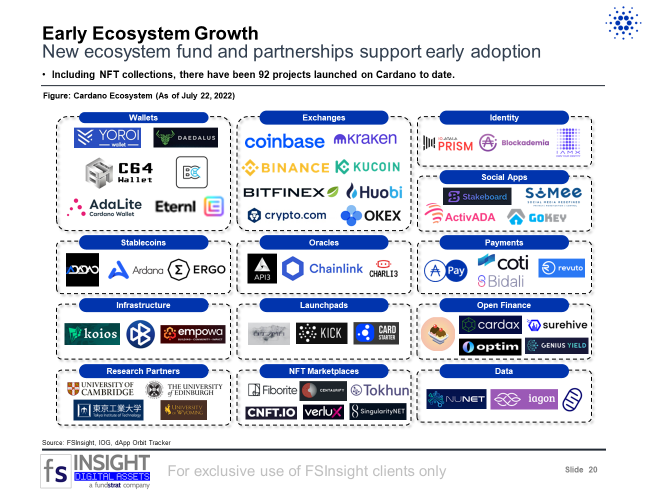
Early Ecosystem Growth (Slide 20)
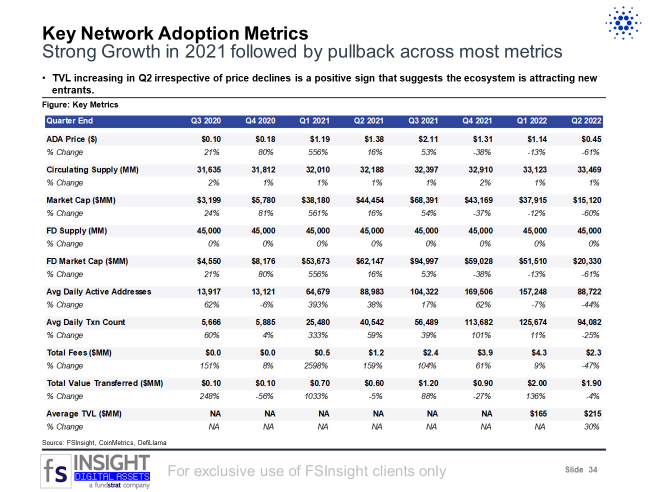
Key Network Adoption Metrics (Slide 34)
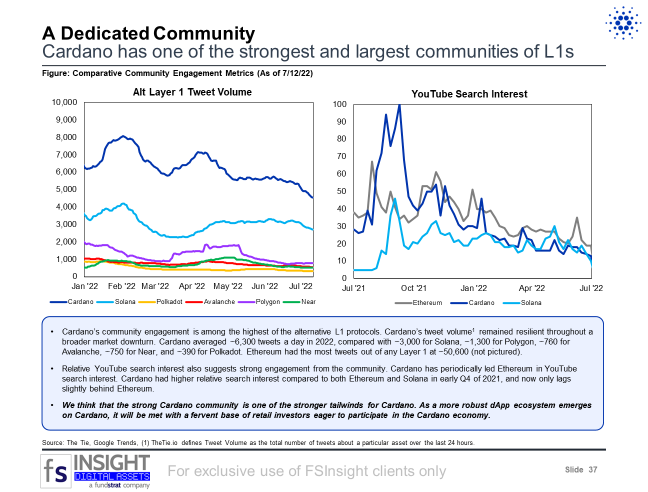
A Dedicated Community (Slide 37)
Risks to Consider (Slide 39)
Articles Read 1/2
Enjoyed the read? Subscribe now for unlimited access!
Get invaluable analysis of the market and stocks. Cancel at any time.
Already have an account? Sign In 83f95a-d7e0e7-37fe5a-ec243e-254aca
Already have an account? Sign In 83f95a-d7e0e7-37fe5a-ec243e-254aca