Bitcoin Mining
Key Takeaways
- Bitcoin mining is the method in which the Bitcoin network is secured and validated. Miners receive a block subsidy reward and transaction fees as compensation for mining blocks. To successfully mine a block, miners are required to solve complex computational puzzles.
- The Bitcoin network targets a new block being processed every 10 minutes. To maintain this pace, a “difficulty adjustment” takes place after every 2016 blocks (approximately every two weeks) that increases or decreases the difficulty for miners to get as close to 10-minute blocks as possible.
- The main business consideration for miners is their cost of production versus the market price of Bitcoin. If a company can mine Bitcoin for cheaper than what they can sell it for on the open market, they are in profit. Other considerations include treasury management, hash rate capacity, Bitcoin halving events, transaction fees, and market outlook.
- Most hash rate is located within the U.S. with large mining companies including Marathon Digital, Cleanspark, Riot Blockchain, and Core Scientific. Marathon Digital is the largest by total hash rate and Cleanspark is one of the most efficient miners from a cash cost of production perspective.
- The upcoming Bitcoin halving event in April will reduce the reward for mining a block from 6.25 BTC to 3.125 BTC. It is expected that the high-cost or low runway miners will be pushed out of the market, presenting opportunities for more efficient miners to expand.
What is Bitcoin Mining?
Bitcoin is known as a proof-of-work (PoW) network. PoW networks require “miners” to solve computational puzzles to add blocks to the blockchain. Miners who supply more computational power to the network have a higher chance of processing a block, and successful miners are compensated with Bitcoin tokens.
Transactions on the Bitcoin network are grouped into blocks, and then block data is put through a cryptographic algorithm known as “hashing,” which turns the block data into an encrypted fixed number of characters. Hashes are deterministic, meaning that a data set (block data in this instance) will always return the same hash, ensuring that different parties can validate the accuracy of hashing data. Hashes cannot be reverse-engineered, meaning you cannot replicate the underlying data by starting with a hash. Bitcoin’s hashing function is known as SHA-256.
In order for miners to produce the correct hash, they need to find the correct “nonce.” Nonce is short for a number that can only be used once. Mining requires an extensive guess-and-check process where a miner continually tries additional nonces (which produces new hashes) until they are successful. A miner will start with a nonce of 0, and with each incorrect attempt, add 1. After finding the correct nonce, the miner poses their “proof of work” to the network so they can verify its accuracy. If the block is accepted by the network, it can be added to the blockchain, and the miner is entitled to block subsidy rewards and transaction fees.
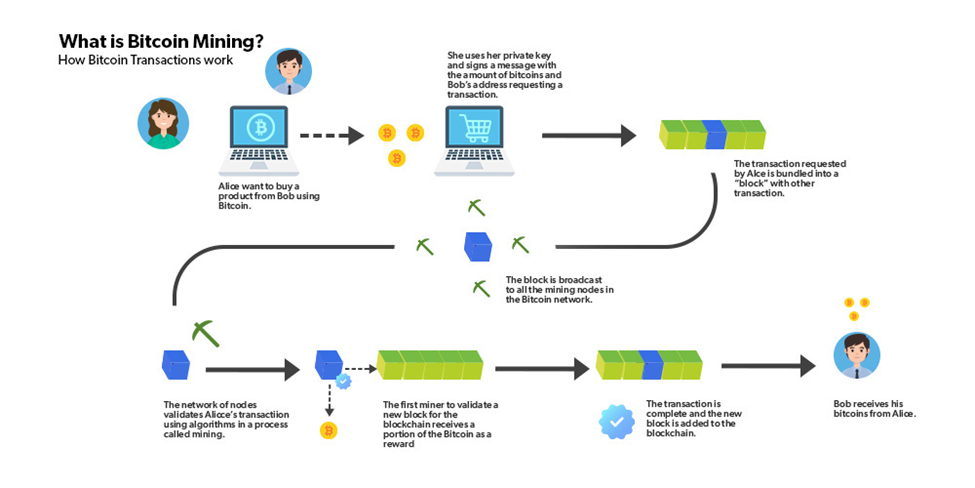
The current subsidy reward for mining a block is 6.25 Bitcoin, which is set to be cut in half with the Bitcoin halving event expected to occur in April. The incentive framework entices new miners to enter the network for their chance to earn Bitcoin while also increasing the decentralization and security of the network.
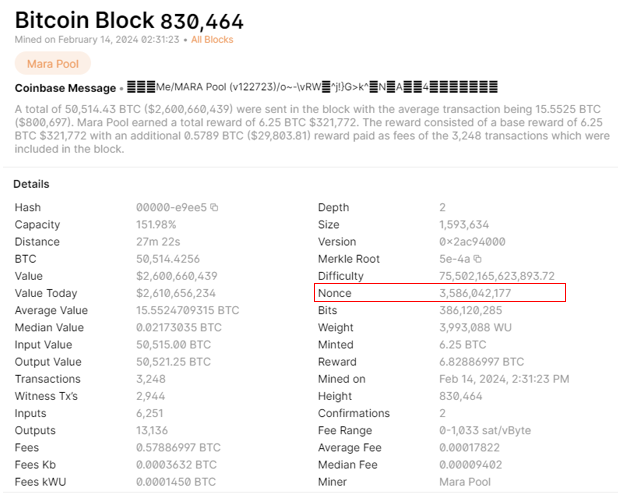
The image above shows a successful block mined by Marathon Digital, one of the largest public Bitcoin miners. The above block had a nonce of 3,586,042,177, displaying how difficult Bitcoin mining has become, considering nonces begin at zero. The number of guesses a miner can make per second is known as “hash rate.” A higher hash rate indicates higher computational power and increases mining efficiency.
The Bitcoin network targets a new block being processed every 10 minutes. To maintain this pace, a “difficulty adjustment” takes place after every 2016 blocks (approximately every two weeks) that increases or decreases the difficulty for miners to get as close to 10-minute blocks as possible. The difficulty adjustment scales with the network’s total hash rate and attempts to keep a balance between hash rate and block processing times.
Mining Business Considerations
High-Level Business Model
When examining the business model of Bitcoin miners, the main consideration is the cost of production versus the market price of Bitcoin. If a company can mine Bitcoin for cheaper than what they can sell it for on the open market, they are in profit.
The main components in the cost of production are hardware and energy costs. As displayed in the previous section, it has become increasingly difficult to mine a block, raising the cost of production for miners. In order to increase hash rate, miners need significant hardware in the form of ASICs, CPUs, and GPUs. Secondly, all that hardware consumes significant electricity as mining is a 24/7 process. Companies can fluctuate the amount of hash rate they provide to the network to scale with current network difficulty and Bitcoin prices.
Treasury Management
There are different metrics to evaluate Bitcoin’s valuation in respect to total security spend by miners, particularly market-cap-to-thermocap. Thermocap is the aggregate amount of tokens paid to miners and serves as a proxy for mining resources spent. A lower ratio indicates Bitcoin offering more value whereas a higher ratio signifies a potentially frothier market. Miners can use data like this to determine the best times to hold or sell mined bitcoin or to adjust how much hash rate capacity to utilize.
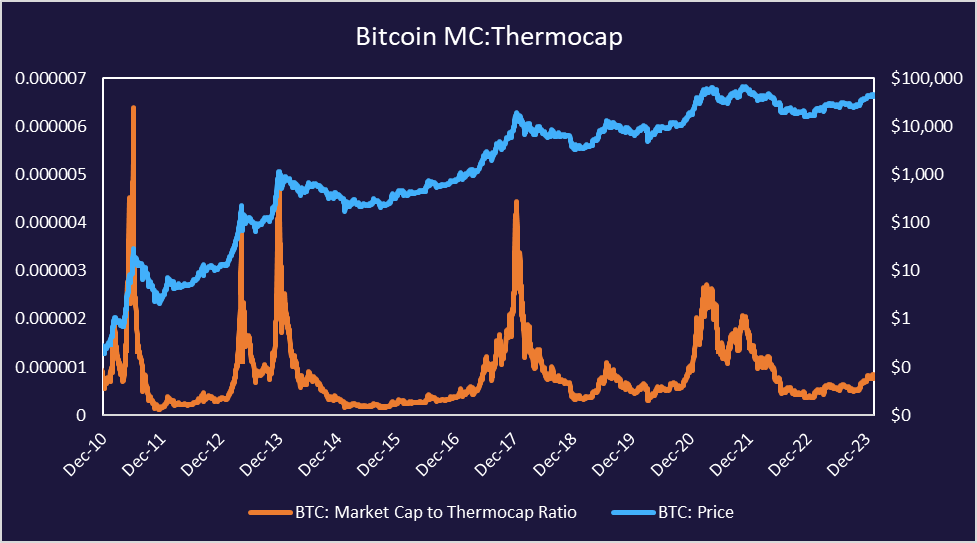
Although Bitcoin’s current market-cap-to-thermocap has emerged from deep value levels, it still presents an optimistic picture for the next twelve to twenty-four months. It’s also worth noting that in each cycle the peaks in MC:Thermocap have been decreasing. It’ll be interesting to monitor if the trend continues in the current cycle.
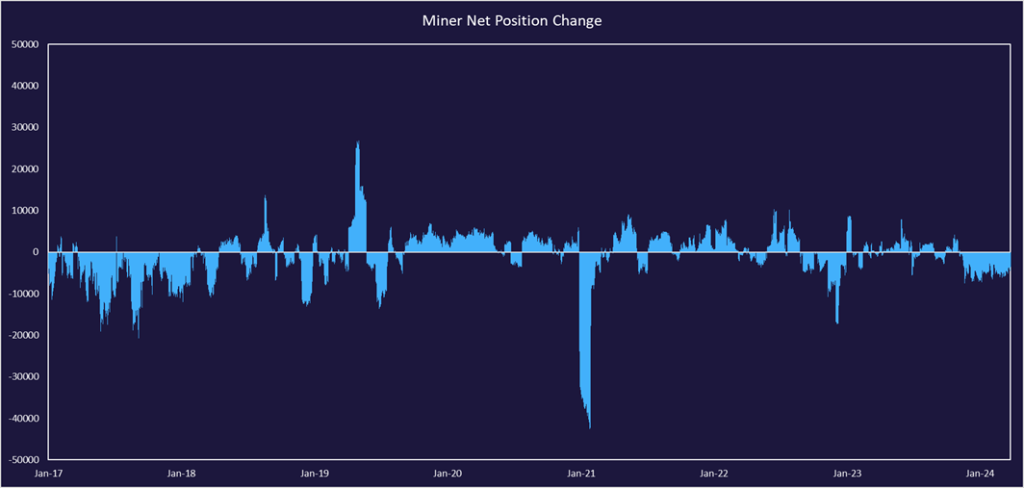
Recent months have shown miners’ net position decreasing, meaning they are selling mined Bitcoin. This is likely attributed to steadying their balance sheets in anticipation of the halving and potentially needing cash on-hand for expansions or to compensate for decreases in revenues. It’s also important to note that Bitcoin has reached new all-time highs and presents a more opportune moment to sell lower-cost Bitcoin. Having more cash on hand can give miners more flexibility to take advantage of potentially distressed miners after the halving or to speculate on further Bitcoin price appreciation.
The Bitcoin Halving
The Bitcoin halving is expected to occur in April 2024. The halving will directly impact Bitcoin miners as the amount of block rewards will be reduced from 6.25 bitcoin to 3.125, cutting potential miner revenue in half. A reduction in block rewards directly impacts the economics of being a profitable miner and will likely result in less efficient miners being pushed out of the market.
With that said, Bitcoin price action following the halving has historically been very bullish, directly reducing the amount of new Bitcoin coming to market, making Bitcoin a scarcer asset. The improved supply dynamics have helped fuel price appreciation following the halving, offsetting some of the revenue reductions from a smaller block reward.
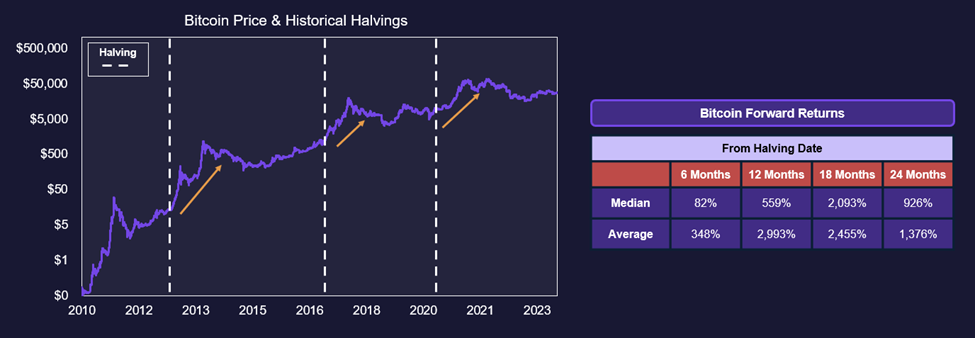
It is a small sample size with only three halving events since Bitcoin’s inception, but it is widely expected to serve as a positive catalyst.
Ordinals & Bitcoin DeFi
Historically, the main incentive for Bitcoin miners has been the block rewards, but over the past year there has been an explosion of Bitcoin ecosystem activity with the creation of Ordinals and more development of Bitcoin DeFi. Transaction fees are becoming a more substantial part of miner revenue as demand for block space continues to rise.
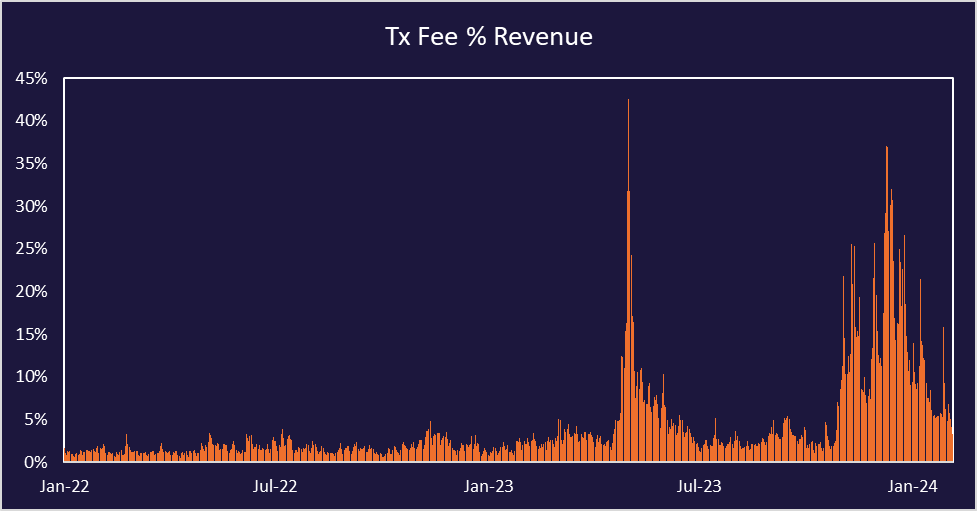
If Bitcoin trends continue, this could provide a tailwind for miners with increased revenue from fees or allowing them to utilize less hash rate capacity and hold revenues constant. Additionally, Bitcoin DeFi is picking up steam with more layer-2 networks being built on top of Bitcoin. Total Value Locked on Bitcoin continues to rise, reaching close to $1 billion early this year.
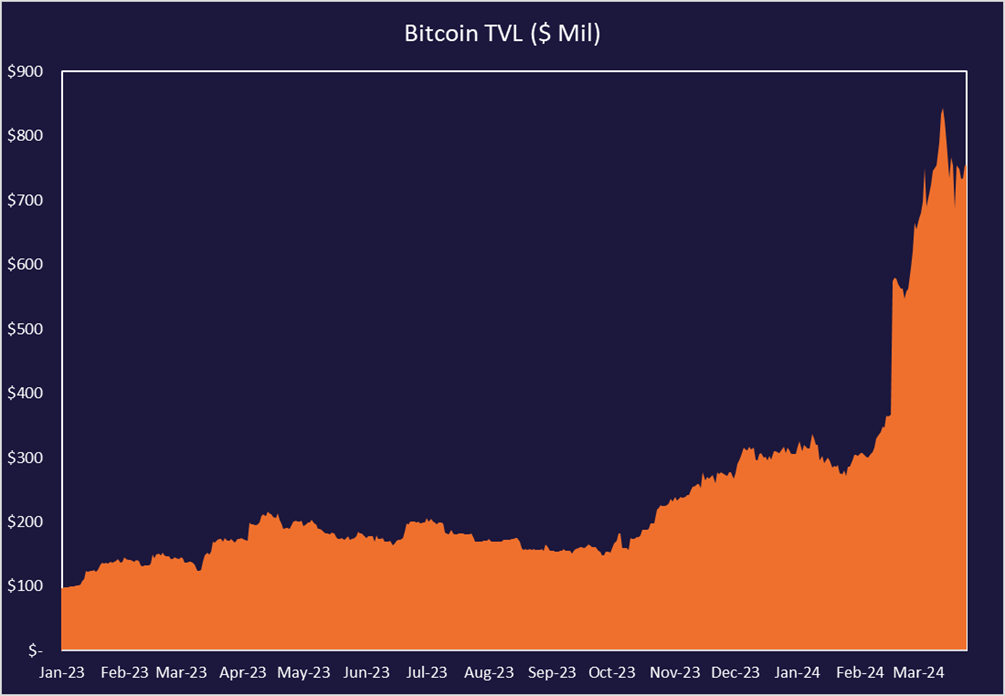
When considering Bitcoin’s current market cap to thermocap ratio, historical halving trends, defi activity, and the current macro backdrop with recent ETF approvals and the likelihood of interest rate cuts in 2024, there are plenty of reasons to be constructive on Bitcoin and Bitcoin miners.
Market Landscape
Since Bitcoin is a decentralized network, anyone with the proper hardware and software can enter the network and begin mining. As such, the total hash rate and difficulty of mining a block has increased substantially over the few years.
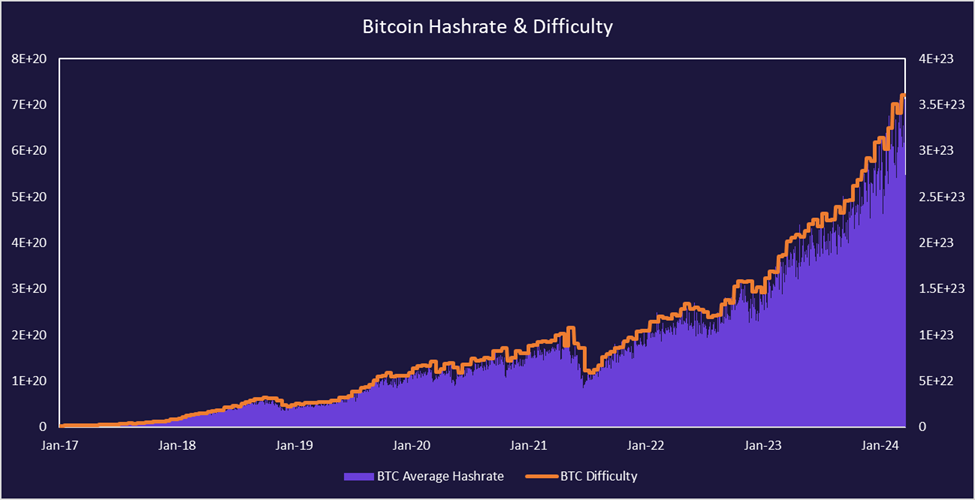
Mining has become a global phenomenon and is not unique to any specific country. The United States is currently the leader in total hash rate, followed by China. China officially banned Bitcoin mining in 2021 but they still contribute a significant amount of global hash rate.
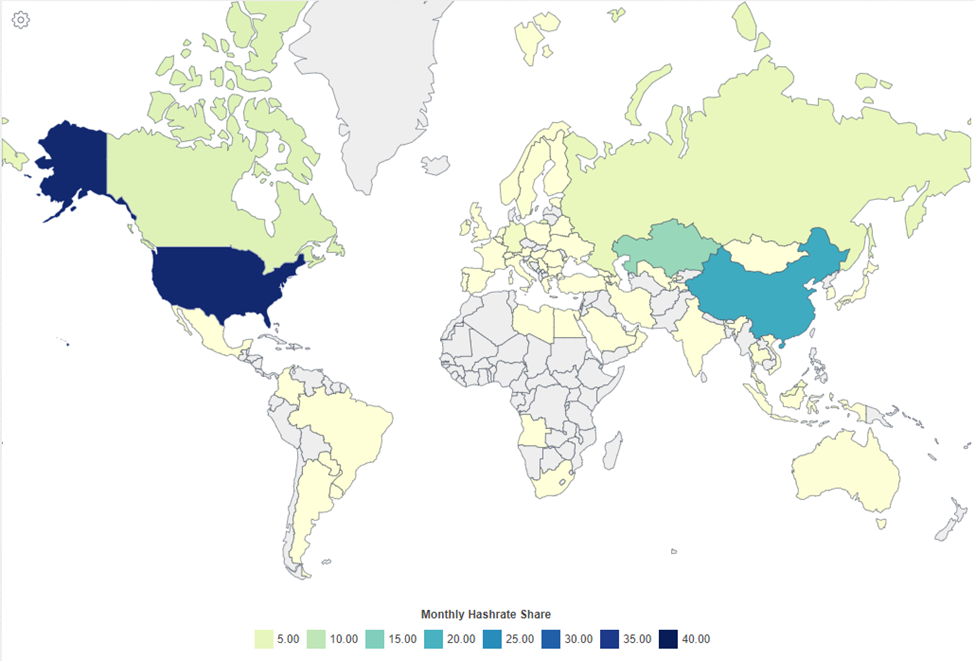
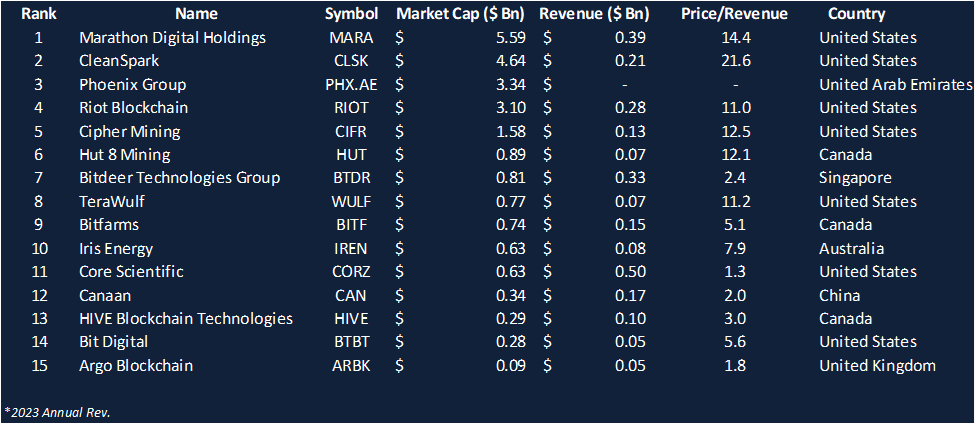
As mentioned, most of the hash rate comes from the USA. Logically, 7 out of the largest 15 Bitcoin mining companies are also domiciled in the USA. Marathon Digital is the largest from both a market capitalization perspective and a hash rate perspective, with an average operational hash rate of 22.4 exahashes/second as of December 2023.
Coinshares conducted an analysis of the halving’s likely effect on U.S. public miners and what it would do to each’s cost structure. Cleanspark is expected to have the lowest cost of production at approximately $27k per bitcoin, followed by Bitfarms and Comint. Marathon and Riot are two of the largest miners but are middle of the pack in estimated cash costs, between $40-50k.
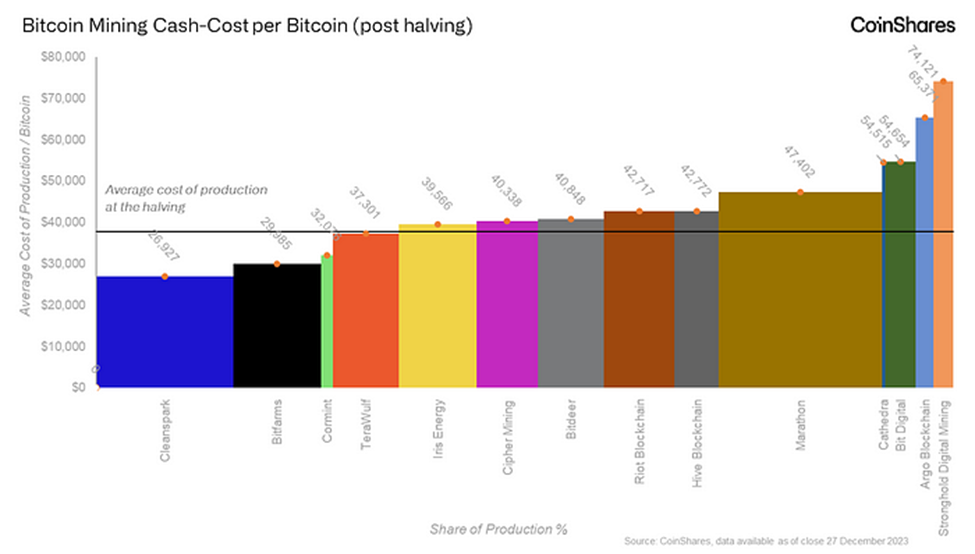
The estimated average cost of production for the entire group came out to $37.9k. At the time of writing, Bitcoin’s price is approximately $69.8k, representing a post-halving 84% profit margin for each marginal Bitcoin mined.
Coinshares also examined which mining companies have the largest runways, or funds on hand to pay for operational expenses. Riot is the clear winner in this category, followed by Marathon, which both have substantial amounts of cash and bitcoin reserves to dip into should Bitcoin turn down for a prolonged period.
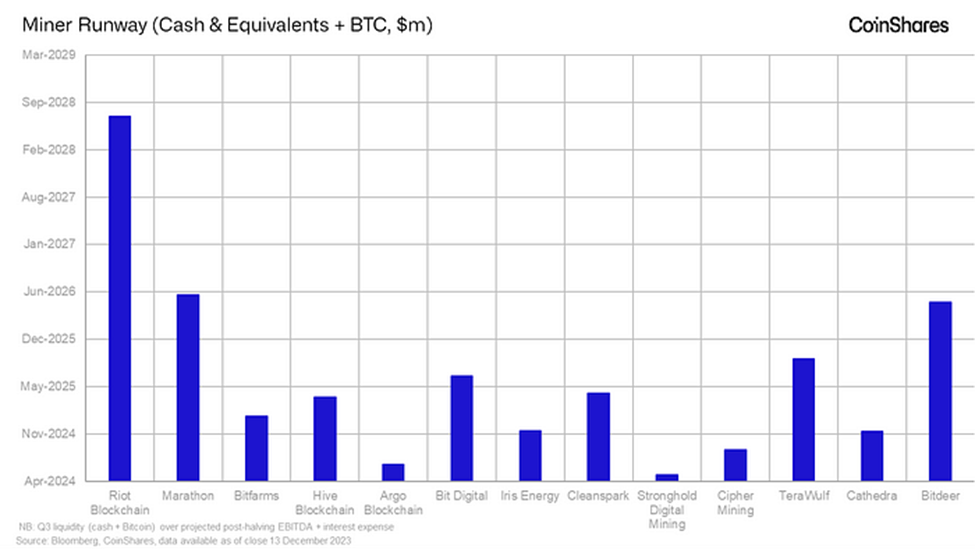
The miners with little runway and a higher cost of production like Stronghold Digital Mining and Bit Digital could face problems if Bitcoin’s price doesn’t appreciate significantly or if they can’t lower their cost of production. Low runway companies have an increased risk of issuing additional equity and diluting shareholders. More than a few miners have done so over the last six months, likely ensuring they have adequate runway ahead of the bull market.
Other Considerations
A common question about Bitcoin and Bitcoin mining is what happens when all 21 million Bitcoin are issued? This poses the question of what incentive miners will have to secure the network after block rewards are depleted. The most common response is that by the time the block subsidy gets to zero (last halving is expected in 2140) the price of Bitcoin combined with the amount of transaction fees should be enough of an incentive for miners. This is highly speculative, and no one knows for sure, but if Bitcoin is still widely used 100 years from now, it is not a ridiculous theory. It is also encouraging to see the transaction fee trends over the last year beginning to represent a larger portion of miner revenues. As activity on Bitcoin continues growing, so should the significance of transaction fees.
There is also a lot of controversy around the amount of energy that Bitcoin mining consumes and the effects on the environment. A lot of the claims on the topic are blown out of proportion. According to estimates by Daniel Betten, 53% of Bitcoin mining operations are sourced from sustainable energy sources. A lot of mining projects in the USA are being built in remote areas where a lot of electric energy gets trapped on the grid. The mining operations use energy that would otherwise be wasted. Additionally, companies are beginning to use Bitcoin mining to improve the economics of energy projects. For example, the Volcano Energy Project in El Salvador is leveraging the country’s surplus of renewable energy to mine Bitcoin and use the profits to invest in their energy infrastructure.
Conclusion
Bitcoin mining is the method in which the Bitcoin network is secured and validated. Miners receive a block subsidy reward and transaction fees as compensation for mining blocks. As long as miners can produce Bitcoin cheaper than they can sell it on the open market, they are profitable. Other considerations for mining companies include treasury management, transaction fees, market outlook, and Bitcoin halving events. Most of the largest miners are located within the U.S., with Marathon Digital being the largest by market capitalization and total hash rate. When examining miners from a cost of production standpoint (post-halving estimates), Cleanspark has the lowest cash cost per Bitcoin at approximately $27k, and the average estimated cost across the evaluated peer group is $37.9k. Should Bitcoin’s price fall below $38k, higher cost miners will likely need to eat into their runway or dilute shareholders to remain afloat.


